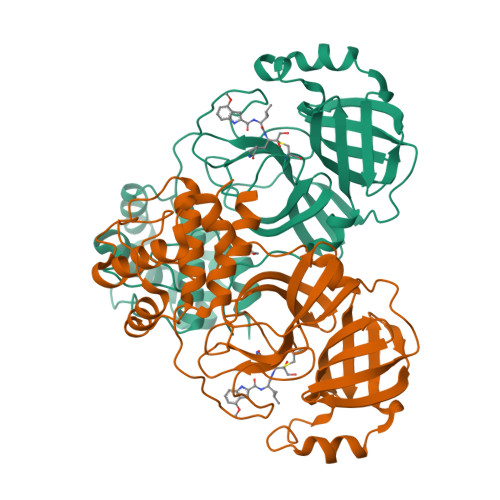
Discovery of Ketone-Based Covalent Inhibitors of Coronavirus 3CL Proteases for the Potential Therapeutic Treatment of COVID-19.
Hoffman, R.L., Kania, R.S., Brothers, M.A., Davies, J.F., Ferre, R.A., Gajiwala, K.S., He, M., Hogan, R.J., Kozminski, K., Li, L.Y., Lockner, J.W., Lou, J., Marra, M.T., Mitchell Jr., L.J., Murray, B.W., Nieman, J.A., Noell, S., Planken, S.P., Rowe, T., Ryan, K., Smith 3rd, G.J., Solowiej, J.E., Steppan, C.M., Taggart, B.(2020) J Med Chem 63: 12725-12747
- PubMed: 33054210
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01063
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6XHL, 6XHM, 6XHN, 6XHO - PubMed Abstract:
The novel coronavirus disease COVID-19 that emerged in 2019 is caused by the virus SARS CoV-2 and named for its close genetic similarity to SARS CoV-1 that caused severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2002. Both SARS coronavirus genomes encode two overlapping large polyproteins, which are cleaved at specific sites by a 3C-like cysteine protease (3CL pro ) in a post-translational processing step that is critical for coronavirus replication. The 3CL pro sequences for CoV-1 and CoV-2 viruses are 100% identical in the catalytic domain that carries out protein cleavage. A research effort that focused on the discovery of reversible and irreversible ketone-based inhibitors of SARS CoV-1 3CL pro employing ligand-protease structures solved by X-ray crystallography led to the identification of 3 and 4 . Preclinical experiments reveal 4 ( PF-00835231 ) as a potent inhibitor of CoV-2 3CL pro with suitable pharmaceutical properties to warrant further development as an intravenous treatment for COVID-19.
Organizational Affiliation:
Pfizer Worldwide Research and Development, 10770 Science Center Drive, San Diego, California 92121 United States.